PFAS Waste Management in Industrial Operations to Minimize Environmental Harm
PFAS Waste Management in Industrial Operations to Minimize Environmental Harm
Blog Article
How PFAS Treatment Makes Sure Tidy and Sustainable Water
The existence of PFAS, generally called "permanently chemicals," presents considerable obstacles to water quality and public wellness. Advanced therapy technologies, consisting of triggered carbon adsorption and membrane filtration, have arised as effective services to mitigate these pollutants. By utilizing these techniques, neighborhoods can not only achieve cleaner water however likewise foster sustainable techniques that protect ecological communities. Nevertheless, the implications of these treatments extend past instant wellness benefits; they raise vital questions about lasting water monitoring methods that need to be dealt with to make sure a durable future. What does this mean for our technique to water sustainability?
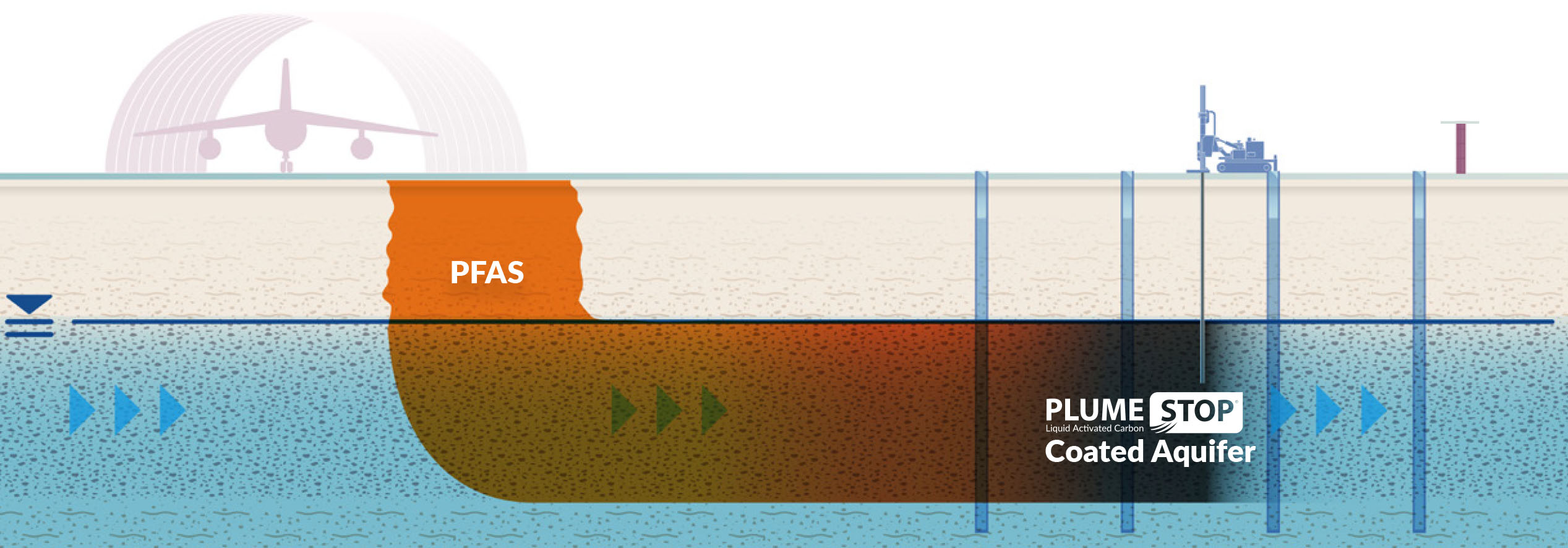
Comprehending PFAS Contamination
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, have arised as a considerable environmental issue due to their prevalent prevalence and perseverance in the atmosphere. These synthetic chemicals have actually been used in various commercial applications and consumer products, consisting of non-stick pots and pans, waterproof garments, and food packaging, due to their special residential properties such as water and oil resistance.
The contamination of soil and water resources by PFAS takes place primarily via industrial discharges, firefighting foam usage, and seeping from garbage dumps. pfas management. As soon as released, these compounds are resistant to destruction, causing their build-up in the environment. This perseverance raises essential problems, as PFAS can travel fars away via groundwater and surface water supply, affecting drinking water supplies and communities

Health And Wellness Risks of PFAS
The perseverance of PFAS in the environment raises substantial health and wellness problems for people exposed to these substances. Research study has actually linked PFAS direct exposure to different damaging wellness impacts, consisting of immune system dysfunction, liver damage, and increased danger of specific cancers.
The universality of PFAS in consumer products, such as non-stick cookware, water-repellent textiles, and food packaging, further intensifies the threat of exposure. Consuming alcohol water infected with PFAS is a considerable worry, as these chemicals can seep right into groundwater sources. Prone populations, including youngsters and those living near industrial websites, might face heightened threats due to their developing systems and possible for higher exposure levels.
As understanding of these health and wellness dangers remains to expand, regulatory firms are beginning to establish guidelines for PFAS levels in drinking water. Public health initiatives are vital to minimize direct exposure and shield areas from the lasting effects of these dangerous compounds.

Innovative Treatment Technologies
Exactly how can we effectively tackle the difficulties positioned by PFAS contamination in water sources? Innovative therapy innovations are becoming crucial solutions in the mission for tidy water. These methods concentrate on the removal or devastation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which are infamous for their determination in the setting.
One appealing strategy is adsorption using advanced materials, such as activated carbon and ion exchange materials. These products have shown efficiency in capturing PFAS molecules from water. One more noteworthy innovation is membrane layer filtration, which makes use of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis to different contaminants at the molecular degree, thus providing an obstacle versus PFAS.
In addition, progressed oxidation procedures (AOPs) employ solid oxidants to damage down PFAS substances right into safe by-products. This technique is particularly reliable for dealing with highly infected water resources. Bioremediation methods, utilizing certain microorganisms, are additionally being checked out to break down PFAS.
As study continues, crossbreed like it systems that combine several innovations may use boosted performance, resolving the intricacies of PFAS contamination. The advancement and implementation of these ingenious treatment technologies are necessary steps towards guaranteeing the safety and sustainability of our water sources.
Advantages of Efficient PFAS Treatment
Efficiently dealing with PFAS contamination in water resources considerably improves public health and wellness and ecological safety and security. PFAS, typically described as "for life chemicals," are immune to destruction and can collect in the body, leading to significant health dangers such as cancer cells, liver damage, and body immune system disorder. By executing effective therapy methods, imp source neighborhoods can decrease exposure to these hazardous materials, ultimately improving the health end results of their populaces.
Furthermore, effective PFAS treatment adds to the preservation of neighborhood ecosystems. Contaminated water can adversely impact aquatic life and interfere with the delicate balance of local environments. By ensuring tidy water, therapy processes protect biodiversity and maintain environmental integrity.
In addition, efficient PFAS remediation can foster public confidence in water quality. When areas are assured that their drinking water is without dangerous pollutants, it advertises a sense of safety and security and well-being. This trust is crucial for neighborhood involvement and assistance for recurring water administration initiatives.
Future of Water Sustainability
Amidst growing worries concerning water quality and shortage, the future of water sustainability depends upon innovative strategies and joint efforts. As areas face the looming dangers of contaminants like PFAS, the advancement of innovative treatment technologies is crucial. These technologies not just concentrate on the removal of hazardous compounds yet also advertise the reuse and recycling of water, consequently reducing total demand.
In addition, effective water governance plays an important duty in ensuring sustainable methods. Policymakers should incorporate clinical research study with regulatory structures to develop clear guidelines for water usage and treatment. Stakeholder involvement, consisting of regional communities and sectors, promotes a sense of shared duty and encourages lasting practices across numerous sectors.
Investment in framework is likewise crucial; upgrading aging systems to include modern-day filtering and filtration approaches can considerably enhance water top quality. Accepting eco-friendly modern technologies, such as all-natural purification systems, can supply environment-friendly solutions.
Eventually, the future of water sustainability exists in an all natural technique that get more combines modern technology, policy, and community involvement. By prioritizing these components, we can protect our water sources for generations ahead, ensuring tidy and lasting water for all.
Final Thought
Finally, the effective therapy of PFAS is important for making sure tidy and lasting water. By employing sophisticated innovations such as turned on carbon adsorption, membrane filtration, and progressed oxidation processes, communities can considerably decrease the wellness risks connected with these pollutants. Moreover, the integration of these therapy approaches sustains ecological community security and boosts biodiversity. Inevitably, durable PFAS therapy techniques add to long-lasting resilience in water monitoring, cultivating public count on water high quality and promoting lasting methods.
Report this page